What Is Google Core Web Vitals Algorithm?
Understand the Google Core Web Vitals Algorithm.
Google Core Web Vitals Algorithm is a ranking-related system that evaluates how real users experience a web page in terms of speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. Instead of focusing only on keywords or backlinks, Google now pays close attention to how comfortable and smooth a website feels when someone actually uses it. This shift reflects Google’s long-term goal of rewarding websites that provide helpful, reliable, and user-friendly experiences.
Over the years, search behavior has changed. Users expect pages to load quickly, respond instantly, and remain stable while they read or interact. As a result, Google introduced Core Web Vitals as part of its broader Page Experience framework. These metrics help Google understand whether a page is frustrating or pleasant for visitors, which directly impacts trust, engagement, and long-term visibility.
Understanding the Three Core Web Vitals Metrics
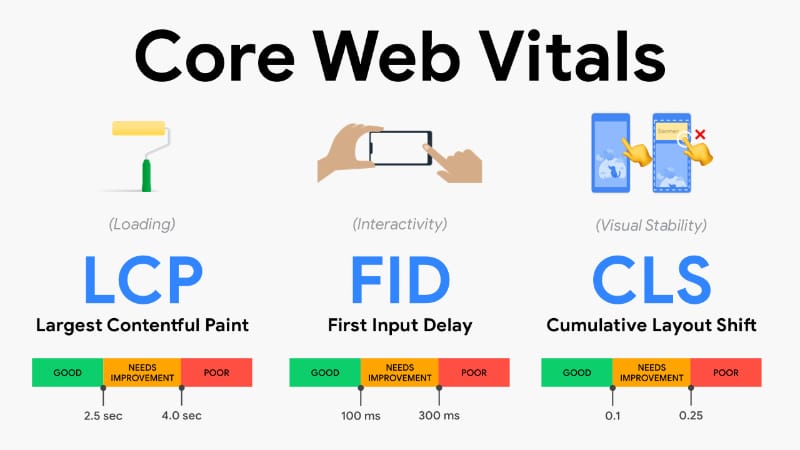
At the heart of the Core Web Vitals Algorithm are three key metrics. Each one focuses on a different aspect of user experience. Together, they form a balanced view of page performance.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Largest Contentful Paint measures loading performance. Specifically, it tracks how long it takes for the largest visible element on a page to load, such as a main image, video, or large block of text. From a user’s perspective, LCP represents the moment when the page feels useful.
A good LCP score is generally within 2.5 seconds. If this metric is slow, users may feel the site is unresponsive, even if smaller elements load quickly. Therefore, optimizing server response times, image delivery, and critical resources plays a key role in improving LCP.
First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay measures interactivity. It calculates the time between a user’s first interaction, such as clicking a button or tapping a link, and the browser’s ability to respond to that interaction. In simple terms, FID shows how responsive a page feels.
A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds. When FID is high, users may feel that the site is frozen or broken. This often happens when the browser is busy executing heavy JavaScript. As a result, managing scripts and reducing main thread work becomes essential for better interactivity.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift measures visual stability. It tracks how much unexpected movement occurs on a page while it is loading. For example, if text suddenly jumps down because an image loads late, that contributes to CLS.
A good CLS score is below 0.1. Visual instability can be frustrating, especially when users accidentally click the wrong element due to shifting content. Therefore, defining image dimensions and avoiding late-loading elements helps maintain a stable layout.
How Core Web Vitals Fit Into Google’s Ranking System
Core Web Vitals are not independent ranking factors. Instead, they function as part of Google’s broader Page Experience signal, which also considers elements such as mobile friendliness, HTTPS security, safe browsing, and the absence of intrusive interstitials. While content relevance continues to be the strongest ranking signal, page experience can act as a deciding factor when multiple pages deliver similar informational value.
In competitive search environments, even small improvements in usability and performance can create meaningful visibility differences, a reality closely observed by manyDigital Marketing Companies in USA while analyzing ranking behavior. As a result, Core Web Vitals guide website owners toward balancing high-quality content with smooth, reliable user experiences that support long-term search performance.
The Role of Real User Data
One of the most important aspects of the Core Web Vitals Algorithm is its reliance on real user data. Google uses anonymized data from the Chrome User Experience Report to understand how pages perform in real conditions.
Conclusion
Google Core Web Vitals Algorithm represents a significant step toward a more user-focused web. By measuring loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, Google encourages websites to prioritize real experiences over surface-level optimization. These metrics do not replace quality content, but they support it by ensuring that valuable information is delivered smoothly and reliably.
As user expectations continue to rise, Core Web Vitals provide a clear framework for building websites that feel fast, stable, and responsive. By understanding and respecting these principles, website owners can create digital spaces that serve users first, while remaining aligned with Google’s evolving standards.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of Google Core Web Vitals?
Google Core Web Vitals aim to measure real user experience on websites. They focus on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability to ensure that pages feel smooth and reliable. By using real user data, Google can better understand whether a site provides a comfortable experience, which helps align search results with user satisfaction and long-term trust.
Do Core Web Vitals directly affect Google rankings?
Core Web Vitals are part of Google’s Page Experience signals, not standalone ranking factors. They do not override content relevance, but they can influence rankings when multiple pages offer similar value. In competitive situations, a page with better user experience metrics may perform slightly better because it provides a smoother and more reliable experience.
How can beginners check their Core Web Vitals performance?
Beginners can start with Google Search Console, which provides a Core Web Vitals report based on real user data. PageSpeed Insights is also useful, as it combines lab tests with field data. These tools clearly show which pages need improvement and explain the underlying issues in an easy-to-understand way.
Why does visual stability matter so much for users?
Visual stability matters because unexpected movement can confuse and frustrate users. When content shifts while someone is reading or interacting, it disrupts focus and can lead to accidental clicks. By maintaining a stable layout, websites feel more predictable and trustworthy, which improves overall user confidence and comfort.
Are Core Web Vitals metrics fixed or likely to change?
Core Web Vitals metrics can evolve over time. Google regularly reviews how users interact with the web and updates its measurements accordingly. For example, new metrics may replace older ones to better reflect real interactions. This flexibility ensures that performance standards stay relevant as technology and user expectations continue to change.

